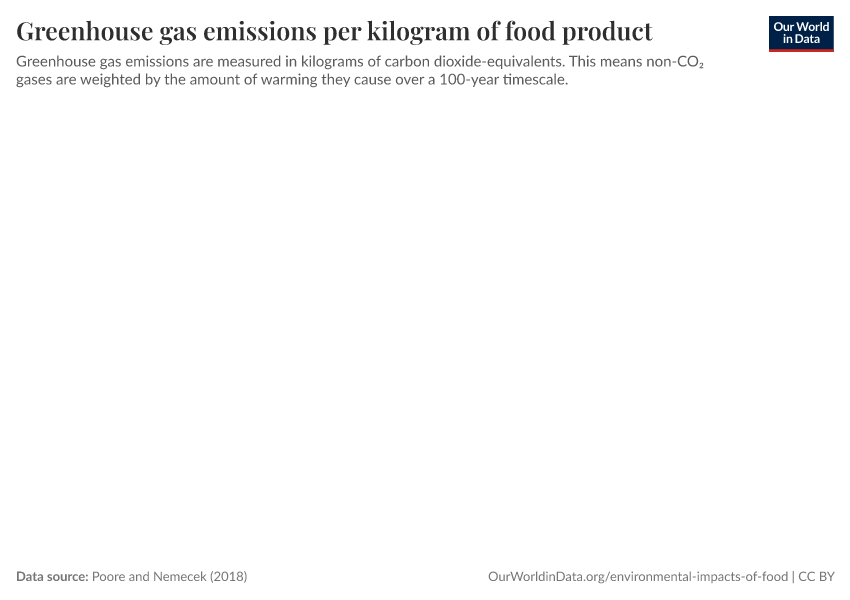
Interactive visualization requires JavaScript
Related research and data
Charts
- Agri-environmental policies weighted by their intensity
- Carbon opportunity costs per kilogram of food
- Environmental footprints of dairy and plant-based milks
- Eutrophying emissions per 100 grams of protein
- Eutrophying emissions per 1000 kilocalories
- Eutrophying emissions per kilogram of food product
- Excess nitrogen from croplands
- Excess nitrogen per hectare of cropland
- Food loss index
- Food waste per capita
- Food: emissions from production and the supply chain
- Food: greenhouse gas emissions across the supply chain
- Freshwater use per kilogram of farmed seafood
- Freshwater withdrawals of foods per 1000 kilocalories
- Freshwater withdrawals per 100 grams of protein
- Freshwater withdrawals per kilogram of food product
- Global emissions from food by life-cycle stage
- Global food miles by transport method
- Greenhouse emissions per unit of food transported
- Greenhouse gas emissions from food systems
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 100 grams of protein
- Greenhouse gas emissions per 1000 kilocalories
- Greenhouse gas emissions per kilogram of seafood
- Land use of foods per 1000 kilocalories
- Land use per 100 grams of protein
- Land use per kilogram of farmed seafood
- Land use per kilogram of food product
- Nitrogen emissions per tonne of farmed seafood
- Number of agri-environmental policies in place
- Number of agri-environmental policies vs. GDP per capita
- Phosphorus emissions per tonne of farmed seafood
- Progress toward productive and sustainable agriculture
- Scarcity-weighted water use of foods per 1000 kilocalories
- Scarcity-weighted water use per 100 grams of protein
- Scarcity-weighted water use per kilogram of food product
- Self-reported dietary choices by age in the UK
- Share of calories in each food group that are lost or wasted
- Share of food lost in post-harvest processes
- Share of food lost in post-harvest processes by region
- Share of global excess nitrogen from croplands
- Share of global excess phosphorus from croplands
- Share of global food loss and waste by region
- Share of global food miles by transport method
- Share of global greenhouse gas emissions from food
- Share of national greenhouse gas emissions that come from food
- Share of total energy used in agriculture and forestry
- Transport's share of global greenhouse gas emissions from food
- Vegans, vegetarians and meat-eaters: self-reported dietary choices in the UK