Interactive visualization requires JavaScript
Related research and data
Charts
- Average cost of drugs for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis
- Average cost of multi drug-resistant tuberculosis treatment
- Average cost of tuberculosis treatment by type
- Causes of deathIHME
- Death rate from respiratory infectionsIHME, crude
- Death rate from respiratory infectionsIHME, age-standardized
- Death rate from tuberculosis in England and Wales
- Deaths from respiratory infections
- Deaths from tuberculosis including those from HIV/AIDS
- Expected funding for tuberculosis versus required budget
- Global tuberculosis incidence rate, by age
- Incidence and prevalence of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis
- Incidence of tuberculosisIHME
- Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis cases
- Number of deaths from tuberculosisIHME
- Number of deaths from tuberculosis and other diseases in people with HIV/AIDS
- Number of one-year-olds who have received different vaccinations
- Number of people with extensively drug resistant tuberculosis
- Number of people with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis
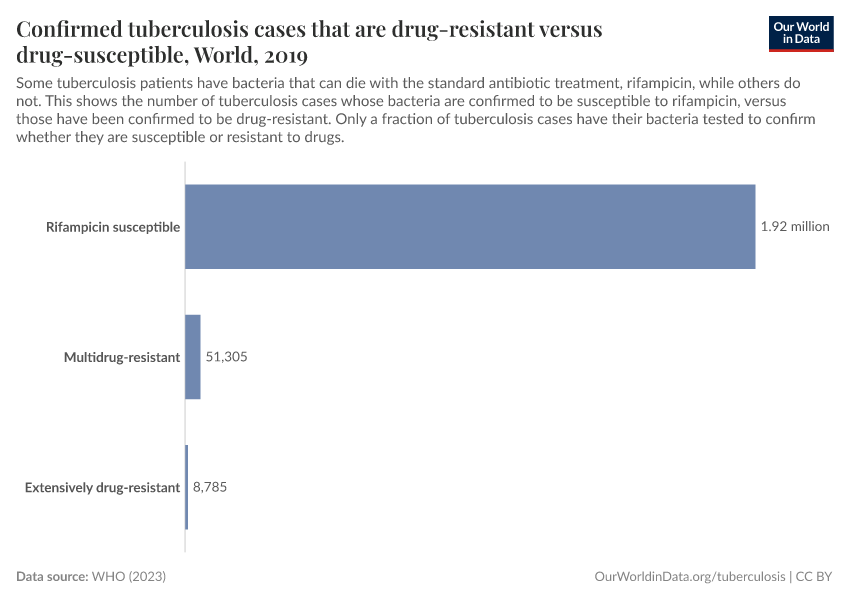
- People living with tuberculosis by drug susceptibility
- Rate of new tuberculosis cases
- Share of newborns vaccinated against tuberculosis
- Share of the population estimated to have prior infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Share of tuberculosis patients with HIV
- Share of tuberculosis tests that are positive
- Sites providing rapid tuberculosis diagnostics per million people
- Tuberculosis case detection rate
- Tuberculosis case fatality rate
- Tuberculosis cases
- Tuberculosis cases attributable to risk factors
- Tuberculosis cases in the United States
- Tuberculosis death rateWHO, age-standardized
- Tuberculosis death rateIHME, crude
- Tuberculosis death rateIHME, age-standardized
- Tuberculosis death rate
- Tuberculosis death rateWHO
- Tuberculosis death rate in people without HIVWHO, crude rate
- Tuberculosis death rate in the United States
- Tuberculosis death rate, by ageIHME, by age group
- Tuberculosis deathsWHO 2023
- Tuberculosis deathsWHO GHE
- Tuberculosis deaths by HIV status
- Tuberculosis deaths by region
- Tuberculosis deaths in children under five
- Tuberculosis deaths in the United States
- Tuberculosis deaths, by age
- Tuberculosis patients living with HIV receiving antiretroviral therapy
- Tuberculosis patients who tested positive for HIV
- Tuberculosis treatment success rate
- Tuberculosis treatment success rate by type
- Tuberculosis-related deaths among people living with HIV