Our vaccination dataset uses the most recent official numbers from governments and health ministries worldwide. Population estimates for per-capita metrics are based on the United Nations World Population Prospects. Income groups are based on the World Bank classification. A full list of our country-specific sources is available at the bottom of this page, and we also answer frequently-asked questions there.
→ Open the Data Explorer in a new tab. Select a group of countries at once: all European countries, 30 largest countries; European Union; Americas; OECD.
The Our World in Data COVID vaccination data
To bring this pandemic to an end, a large share of the world needs to be immune to the virus. The safest way to achieve this is with a vaccine. Vaccines are a technology that humanity has often relied on in the past to bring down the death toll of infectious diseases.
Within less than 12 months after the beginning of the pandemic, several research teams rose to the challenge and developed vaccines that protect from SARS-CoV-2.
Now the challenge is to make these vaccines available to people around the world. It will be key that people in all countries — not just in rich countries — receive the required protection. To track this effort we at Our World in Data are building the international vaccination dataset that we make available on this page. It is updated each morning, with the most recent official numbers up to the previous day.
- Data sources: at the end of this page you find a detailed list of all our country-specific sources.
- Open access: as with all of our data, we are making this dataset openly available, so that everyone can check and use the data that we bring together. You find the vaccination data in our daily-updated repository on GitHub.
Our work belongs to everyone
- All our code is open-source
- All our research and visualizations are free for everyone to use for all purposes
This page has a number of charts on vaccination. In the box below you can select any country you are interested in — or several if you want to compare countries. All charts on this page will then show data for the countries that you selected.
The following charts show the breakdown of people vaccinated, between those who have received only their first vaccine dose, and those who have completed the initial vaccination protocol (2 doses for most vaccines, 1 or 3 for a few manufacturers).
The following map and chart show the number of vaccine doses administered per 100 people within a given population. All doses, including boosters, are counted individually.
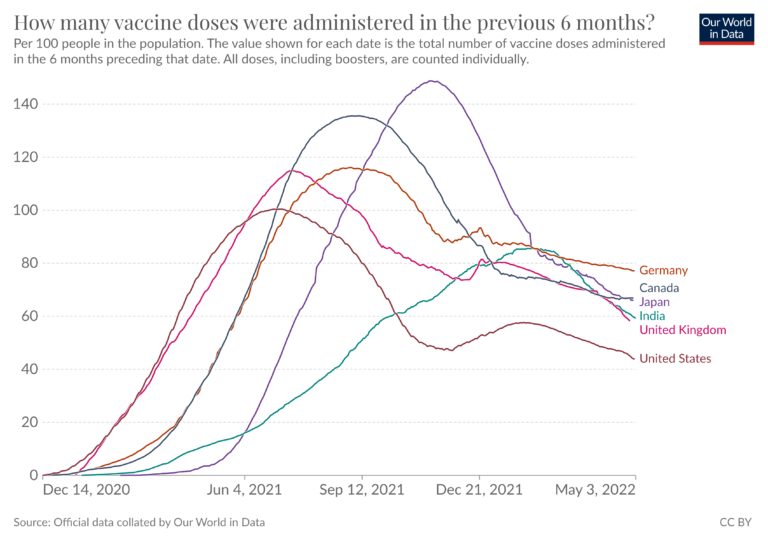
The following chart shows, for each date, the total number of vaccine doses administered in the 12 months preceding that date. This is given per 100 people in the population. All doses, including boosters, are counted individually.
The following chart shows the share of the total population that has received at least one dose of vaccine. This may not equal the share with a complete initial protocol if the vaccine requires two doses. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric goes up by 1. If they receive the second dose, the metric stays the same.
The following chart shows the total number of people that have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. This may not equal the number with a complete initial protocol if the vaccine requires two doses. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric goes up by 1. If they receive the second dose, the metric stays the same.
The following chart shows the share of the total population that has completed the initial vaccination protocol. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric stays the same. If they receive the second dose, the metric goes up by 1.
The following chart shows the total number of people that have completed the initial vaccination protocol. If a person receives the first dose of a 2-dose vaccine, this metric stays the same. If they receive the second dose, the metric goes up by 1.
The following charts show the number of booster doses administered. Booster doses are doses administered beyond those prescribed by the original vaccination protocol — for example, a third dose of Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine, or a second dose of Johnson & Johnson vaccine.
The following charts provide data on the share of people that have been vaccinated against by age group. This is provided as three metrics: the share that has received at least one dose; the share that has completed the initial protocol; and the share that is only partially vaccinated.
This data is only available for countries that report the breakdown of doses administered by first and second doses by age.
The following chart shows the share of the population in each age group that has received at least one dose. This metric includes those that are partly vaccinated or have completed the initial protocol.
The following chart shows the share of the population in each age group that has completed the initial protocol.
The following chart shows the share of the population in each age group that has received a booster dose.
The following chart shows the cumulative number of doses administered, broken down by vaccine manufacturer. This is only available for a select number of countries that report the necessary data.
The following chart shows the daily number of doses administered per 100 people. This is shown as the rolling seven-day average. Note that this is counted as a single dose, and may not equal the total number of people vaccinated, depending on the specific dose regime (e.g. people receive multiple doses).
These charts show the cumulative number of doses donated to the COVAX initiative by different countries, broken down by whether the donations have only been announced, actually donated, or delivered to the recipients. This is only available for a select number of countries for which the COVID-19 Task Force reports the necessary data.
The first chart shows the number of doses donated, while the next three charts show that number adjusted for:
- The population of the donating country;
- The GDP of the donating country;
- The number of doses administered by the donating country to its own population.
COVID-19 Vaccines Global Access (COVAX)
COVAX is a worldwide initiative aimed at equitable access to COVID-19 vaccines directed by Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), and the World Health Organization (WHO). COVAX coordinates international resources to enable low-to-middle-income countries equitable access to COVID-19 tests, therapies, and vaccines.
This interactive chart maps government policies on COVID-19 vaccination. Note that only policies on the availability of vaccinations are tracked. It does not track the number of people who have been vaccinated.
Countries are grouped into six categories:
- No availability
- Availability for ONE of following: key workers/ clinically vulnerable groups / elderly groups
- Availability for TWO of following: key workers/ clinically vulnerable groups / elderly groups
- Availability for ALL of following: key workers/ clinically vulnerable groups / elderly groups
- Availability for all three plus partial additional availability (select broad groups/ages)
- Universal availability
Vaccination policy data is sourced from the Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker
This data on vaccination policies is sourced from the Oxford Coronavirus Government Response Tracker (OxCGRT).
This resource is published by researchers at the Blavatnik School of Government at the University of Oxford: Thomas Hale, Anna Petherik, Beatriz Kira, Noam Angrist, Toby Phillips and Samuel Webster.
The tracker presents data collected from public sources by a team of over one hundred Oxford University students and staff from every part of the world.
The data presented here is taken directly from the OxCGRT project; we at Our World in Data don’t track policy responses ourselves and we don’t make additions to the tracker’s dataset.
These charts are regularly updated based on the latest version of the response tracker.
OxCGRT is an ongoing collation project of live data. If you see any inaccuracies in the underlying data, or for specific feedback on the analysis or another aspect of the project please contact OxCGRT team. See the tracker’s notes and guidance on data quality.
The Imperial College London YouGov Covid-19 Behaviour Tracker Data Hub has gathered global insights on people’s behaviors in response to COVID-19 throughout the pandemic. This survey covers public behaviors and attitudes ranging from mask-wearing to self-isolation, social distancing, symptoms and testing.
Their dataset on attitudes to vaccination extended from January 2021 until March 2022. You can explore the change in attitudes across countries over time here:
Why do the figures displayed on this page look different from the ones published by my government?
In some cases, the vaccination figures on this page can look different from the ones reported by governments. Most often it is not because of the numerator (number of people vaccinated) but instead because of the denominator (number of people in the population). This usually happens for two main reasons:
- The official data reports the vaccination coverage in terms of the share of people vaccinated in the population eligible for vaccination (very often, among adults only). Our priority is to make our data comparable between countries — regardless of criteria for eligibility, which tend to vary across countries and across time. For this reason, we always use the total population of the country (i.e. people of all ages) as the denominator.
- The official data uses a different population estimate. The population estimates we use come from the United Nations World Population Prospects. We use this data for its reliability, its consistent methods, and because it makes our work much easier (see below for more information). In a few cases, we use other sources when the figures provided by the UN differ substantially from reliable and more recent national estimates.
What population data are the per-capita metrics based on?
The population estimates we use come from the United Nations World Population Prospects. We use this data for its reliability, its consistent methods, and because it makes our work much easier. The exact values can be viewed in our GitHub repository.
The United Nations estimates may not always reflect the latest censuses or national figures—but there are several reasons why we use this data over country-by-country national population estimates.
- The UNWPP dataset is the standard in research. The main reason is that it uses a reliable and standardized methodology for all countries. For example, if we used individual country data, some may include overseas workers, expats, undocumented immigrants, etc. but others wouldn’t.
- Using data from the UN allows us to get accurate population estimates for all territories in the world very easily. Finding and maintaining estimates based on national censuses would be very time-consuming for our small team, without bringing much additional value to our work.
- Other reasons include the availability of yearly data (national censuses are only conducted every few years), and avoiding double-counting in cases of border disputes.
For all these reasons, the UN data is the best solution to bring accurate per-capita metrics to our COVID data. In a few cases, we use other sources when the figures provided by the UN differ substantially from reliable and more recent national estimates.
Can the value of per-capita metrics exceed 100%?
The population estimates we use to calculate per-capita metrics are all based on the last revision of the United Nations World Population Prospects. In a few cases, we use other sources when the figures provided by the UN differ substantially from reliable and more recent national estimates. Additionally, it’s important to bear in mind that in some territories, vaccination coverage may include non-residents (such as tourists and foreign workers). For these reasons, per-capita metrics may sometimes exceed 100%.
What is the definition of a complete initial protocol?
In our data, people with a complete initial protocol are those who have received all doses prescribed by their vaccination regimen (e.g. 2 doses for Pfizer/BioNTech, Moderna, Oxford/AstraZeneca, etc. and 1 dose for Johnson & Johnson, CanSino, etc.).
Some countries also allow for alternative definitions, such as having been infected with SARS-CoV-2 in the past and having received 1 dose of a two-dose regimen. We currently ignore these alternative definitions to preserve the common definition of a complete protocol, i.e. all doses required in the vaccine regimen. This allows for optimal comparability between countries.
What classification are the income groups based on?
The income groups we use come from the World Bank income classification. The exact list of countries can be viewed in our GitHub repository.
Why isn’t my country shown by default on a chart? How do you choose which countries are shown?
Due to the limited space on our charts and the number of countries in the world, unfortunately, we cannot show every country in the world by default. On each chart of this page, therefore we choose a default selection of countries based on a mix of criteria: mainly total population, but also the number of doses administered and share of the population vaccinated. These lists are updated about once a month.
Are participants in vaccine clinical trials included in your data?
We do not include participants in the vaccine arm of clinical trials, as this data is not available for many of the hundreds of trials currently taking place.
How do you report vaccinations performed in Israel and Palestine?
In our dataset and charts on COVID-19 vaccinations, we report vaccinations performed in Israel and Palestine separately.
The vaccination data is needed to understand how the pandemic is evolving. For this, it is key to bring together the vaccination data with data on COVID-19 cases and COVID-19 deaths. Global health institutions that report on the pandemic are reporting these metrics separately:
- The World Health Organization reports the measures for Israel separately from Palestine in its data.
- Johns Hopkins University also reports Israel separately from Palestine in its data on cases & deaths of COVID-19, which has been used worldwide in the last year.
Reporting the data for Palestine and Israel separately also allows us to show their respective reported vaccination levels. It makes clear what the respective vaccination levels are, as reported by the Government of Israel and the Palestinian Ministry of Health.
Finally, our dataset on COVID-19 vaccinations is sourced from official data published by governments and ministries of health from countries around the world. This is also the case for Israel and Palestine. We show figures for Palestine and Israel separately, as they are reported separately by the Government of Israel and the Palestinian Ministry of Health.
The Populations Division of the United Nations reports population figures for countries around the world, and we are relying on their latest data (from their 2019 revision) for countries around the world of. They report a population of 8,655,541 people for Israel and a population of 5,101,416 people for Palestine.
The resulting shares of people vaccinated in Israel and Palestine can be seen in our COVID-19 Data Explorer.
You can download the full dataset alongside the detailed sources on GitHub.
Sign up for regular updates from Our World in Data
→ If you want to keep up-to-date with our work on COVID-19, and the many other topics we cover you can sign up for our newsletter.