Global meat demand if everyone ate like the average citizen of...
What you should know about this indicator
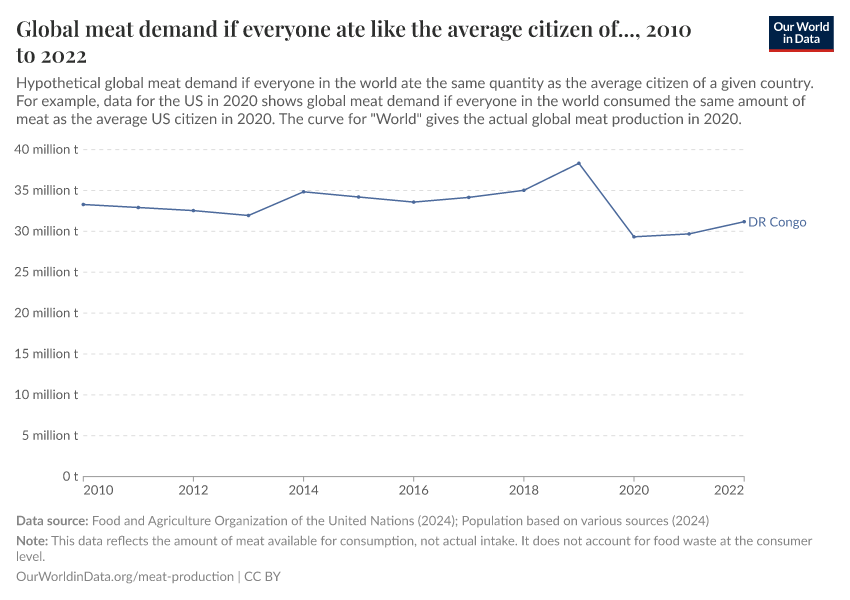
- This is a hypothetical variable derived by Our World in Data which answers the question: "What would global meat demand have to be if everyone in the world consumed the average per capita amount of a given country?". For example: "How much meat would need to be provided if everyone in the world consumed as much meat as the average UK citizen?".
- We do not have data on actual individual consumption. Instead, this data reflects the amount of meat available for consumption. It may include food that is wasted at the consumer level and not eaten.
What you should know about this indicator
- This is a hypothetical variable derived by Our World in Data which answers the question: "What would global meat demand have to be if everyone in the world consumed the average per capita amount of a given country?". For example: "How much meat would need to be provided if everyone in the world consumed as much meat as the average UK citizen?".
- We do not have data on actual individual consumption. Instead, this data reflects the amount of meat available for consumption. It may include food that is wasted at the consumer level and not eaten.
Sources and processing
This data is based on the following sources
How we process data at Our World in Data
All data and visualizations on Our World in Data rely on data sourced from one or several original data providers. Preparing this original data involves several processing steps. Depending on the data, this can include standardizing country names and world region definitions, converting units, calculating derived indicators such as per capita measures, as well as adding or adapting metadata such as the name or the description given to an indicator.
At the link below you can find a detailed description of the structure of our data pipeline, including links to all the code used to prepare data across Our World in Data.
Notes on our processing step for this indicator
- This indicator was calculated by multiplying global population by per capita meat supply of a given country.
Reuse this work
- All data produced by third-party providers and made available by Our World in Data are subject to the license terms from the original providers. Our work would not be possible without the data providers we rely on, so we ask you to always cite them appropriately (see below). This is crucial to allow data providers to continue doing their work, enhancing, maintaining and updating valuable data.
- All data, visualizations, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license. You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
Citations
How to cite this page
To cite this page overall, including any descriptions, FAQs or explanations of the data authored by Our World in Data, please use the following citation:
“Data Page: Global meat demand if everyone ate like the average citizen of...”, part of the following publication: Hannah Ritchie, Pablo Rosado, and Max Roser (2023) - “Agricultural Production”. Data adapted from Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Various sources. Retrieved from https://archive.ourworldindata.org/20260119-070102/grapher/hypothetical-global-meat-demand.html [online resource] (archived on January 19, 2026).How to cite this data
In-line citationIf you have limited space (e.g. in data visualizations), you can use this abbreviated in-line citation:
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2024); Population based on various sources (2024) – with major processing by Our World in DataFull citation
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2024); Population based on various sources (2024) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Global meat demand if everyone ate like the average citizen of... – FAO” [dataset]. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, “Food Balances: Food Balances (-2013, old methodology and population)”; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, “Food Balances: Food Balances (2010-)”; Various sources, “Population” [original data]. Retrieved February 16, 2026 from https://archive.ourworldindata.org/20260119-070102/grapher/hypothetical-global-meat-demand.html (archived on January 19, 2026).