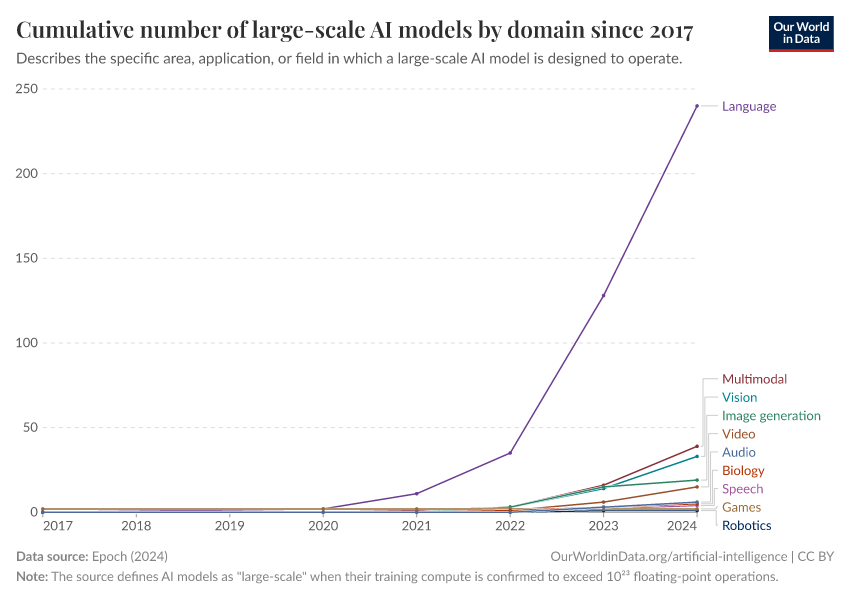
Cumulative number of large-scale AI models by domain since 2017
What you should know about this indicator
- Game systems are specifically designed for games and excel in understanding and strategizing gameplay. For instance, AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, defeated the world champion in the game of Go. Such systems use complex algorithms to compete effectively, even against skilled human players.
- Language systems are tailored to process language, focusing on understanding, translating, and interacting with human languages. Examples include chatbots, machine translation tools like Google Translate, and sentiment analysis algorithms that can detect emotions in text.
- Multimodal systems are artificial intelligence frameworks that integrate and interpret more than one type of data input, such as text, images, and audio. ChatGPT-4 is an example of a multimodal model, as it has the capability to process and generate responses based on both textual and visual inputs.
- Vision systems focus on processing visual information, playing a pivotal role in image recognition and related areas. For example, Facebook's photo tagging model uses vision AI to identify faces.
- Speech systems are dedicated to handling spoken language, serving as the backbone of voice assistants and similar applications. They recognize, interpret, and generate spoken language to interact with users.
- Biology systems analyze biological data and simulate biological processes, aiding in drug discovery and genetic research.
- Image generation systems create visual content from text descriptions or other inputs, used in graphic design and content creation.
What you should know about this indicator
- Game systems are specifically designed for games and excel in understanding and strategizing gameplay. For instance, AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, defeated the world champion in the game of Go. Such systems use complex algorithms to compete effectively, even against skilled human players.
- Language systems are tailored to process language, focusing on understanding, translating, and interacting with human languages. Examples include chatbots, machine translation tools like Google Translate, and sentiment analysis algorithms that can detect emotions in text.
- Multimodal systems are artificial intelligence frameworks that integrate and interpret more than one type of data input, such as text, images, and audio. ChatGPT-4 is an example of a multimodal model, as it has the capability to process and generate responses based on both textual and visual inputs.
- Vision systems focus on processing visual information, playing a pivotal role in image recognition and related areas. For example, Facebook's photo tagging model uses vision AI to identify faces.
- Speech systems are dedicated to handling spoken language, serving as the backbone of voice assistants and similar applications. They recognize, interpret, and generate spoken language to interact with users.
- Biology systems analyze biological data and simulate biological processes, aiding in drug discovery and genetic research.
- Image generation systems create visual content from text descriptions or other inputs, used in graphic design and content creation.
Sources and processing
This data is based on the following sources
How we process data at Our World in Data
All data and visualizations on Our World in Data rely on data sourced from one or several original data providers. Preparing this original data involves several processing steps. Depending on the data, this can include standardizing country names and world region definitions, converting units, calculating derived indicators such as per capita measures, as well as adding or adapting metadata such as the name or the description given to an indicator.
At the link below you can find a detailed description of the structure of our data pipeline, including links to all the code used to prepare data across Our World in Data.
Notes on our processing step for this indicator
The count of large-scale AI models AI systems per domain is derived by tallying the instances of machine learning models classified under each domain category. It's important to note that a single machine learning model can fall under multiple domains. The classification into domains is determined by the specific area, application, or field that the AI model is primarily designed to operate within.
Reuse this work
- All data produced by third-party providers and made available by Our World in Data are subject to the license terms from the original providers. Our work would not be possible without the data providers we rely on, so we ask you to always cite them appropriately (see below). This is crucial to allow data providers to continue doing their work, enhancing, maintaining and updating valuable data.
- All data, visualizations, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license. You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
Citations
How to cite this page
To cite this page overall, including any descriptions, FAQs or explanations of the data authored by Our World in Data, please use the following citation:
“Data Page: Cumulative number of large-scale AI models by domain since 2017”, part of the following publication: Charlie Giattino, Edouard Mathieu, Veronika Samborska, and Max Roser (2023) - “Artificial Intelligence”. Data adapted from Epoch AI. Retrieved from https://archive.ourworldindata.org/20260304-094028/grapher/cumulative-number-of-large-scale-ai-models-by-domain.html [online resource] (archived on March 4, 2026).How to cite this data
In-line citationIf you have limited space (e.g. in data visualizations), you can use this abbreviated in-line citation:
Epoch AI (2025) – with major processing by Our World in DataFull citation
Epoch AI (2025) – with major processing by Our World in Data. “Cumulative number of large-scale AI models by domain since 2017” [dataset]. Epoch AI, “Tracking Compute-Intensive AI Models” [original data]. Retrieved March 7, 2026 from https://archive.ourworldindata.org/20260304-094028/grapher/cumulative-number-of-large-scale-ai-models-by-domain.html (archived on March 4, 2026).